MOTOR TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
COOLING SYSTEM
GENERAL
Transmission Oil Cooler or Heat Exchanger
7. Engine hot spots.
On some trucks equipped with automatic or
8. Need for higher octane fuel.
semiautomatic transmissions, the transmission oil is
Overcooling
The following engine troubles result when an engine
circulated through an oil cooler or heat exchanger
.
is overcooled.
The function of this unit is to control transmission
1. Excessive fuel consumption.
temperature and thereby keep oil in the proper
2. Sludge formation in crankcase.
temperature range for its most efficient lubrication. This
3. Corrosive acids formed in crankcase.
is done either by using engine heat to bring transmission
COOLING SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
temperature up, or by using the cooling system to
Rust Prevention
dissipate any excessive heat generated within the
To keep engines operating to new truck efficiency, all
transmission.
forms of rust formation must be prevented.
The
Leakage due to corrosion or an improper seal will
formation of rust in the cooling system is a result of
cause contamination between cooling system and
water, iron, and oxygen and can only be prevented by
transmission. The effects of this condition are obvious.
maintaining full strength corrosion protection at all times.
For rust protection during the winter months, an
antifreeze having a corrosion preventive should be
installed in the fall. When spring arrives, drain the old
antifreeze solution from the cooling system as all
corrosion inhibitors are weakened and may be entirely
exhausted, depending on how the truck has be en taken
care of and how far and fast it has been driven. To rust
proof the cooling system for summer driving,add a good
EFFECTS OF COOLING SYSTEM NEGLECT
rust inhibitor with the first fill of clean water in the spring.
Whenever an engine does not perform at top
This solution should then be drained in the fall and a
efficiency, a neglected cooling system may be at fault
fresh filling of chemically treated antifreeze installed. A
even though the engine part directly responsible is not
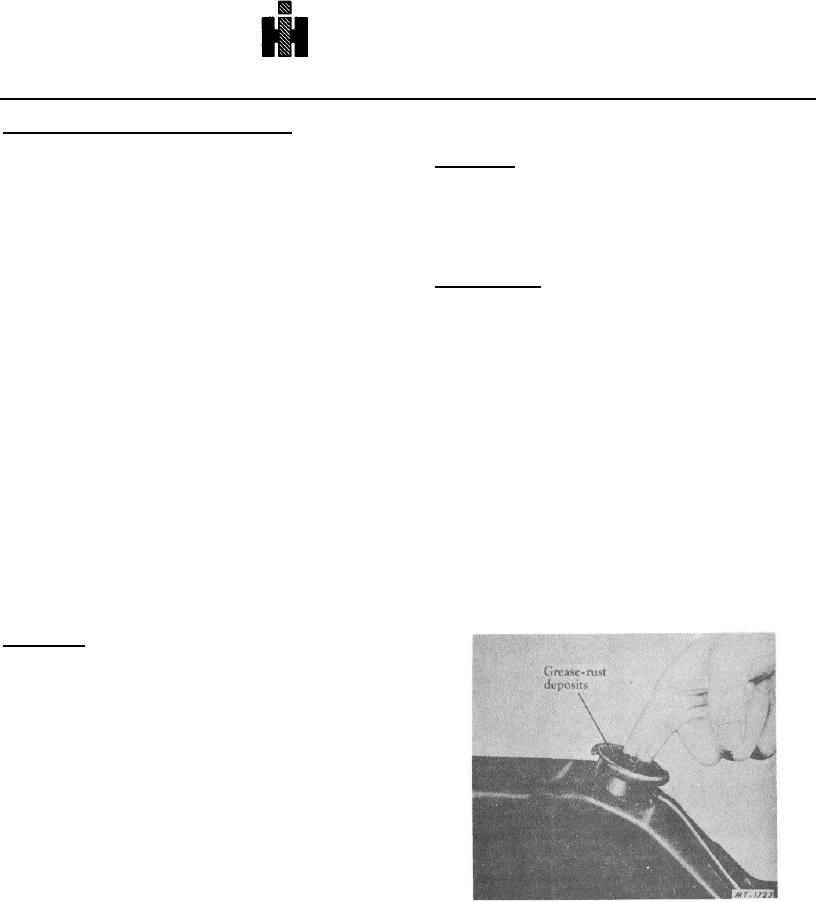
good quick test to determine if cooling system needs
even a part of the cooling system. Most of these ills will
cleaning or flushing due to rust, scale or grease is shown
be traced to overheating; however, an engine that is
in Fig. 5.
running too cold can be just as troublesome.
Overheating
An engine that is overheating may lead to troubles
such as the following:
1. Burned valves.
2. Pinging or knocking.
3. Vapor lock.
4. Poor lubrication increased engine wear.
5. Sticking valve and valve lifters.
6. Short spark plug life.
Fig. 5 Quick Visual Check of Cooling System
241

